
Employ multiple symmetry planes to simulate heat radiation in all directions simultaneously with reduced computational costs Include diffuse and direct solar radiation in surface-to-surface radiation models Use material property data from a library of building and refrigerant materials Develop models involving heat and moisture transport in air with a new physics interface Simulate wells with a new boundary condition that easily defines injection inflows and exploitation outflows Make use of the automatic treatment of flow near walls to switch between different formulations for modeling turbulent flow dependent on mesh resolution Apply the newly available v2-f turbulence model for CFD simulations with strong turbulence anisotropy Utilize the new highly automated and robust algebraic multigrid (AMG) solver for fluid flow New Heat Transfer Modeling Features in COMSOL 5.3 Webinar May 10 Analyze transient thermoviscous acoustics applications Apply perfectly matched layers (PMLs) for absorbing outgoing waves in time-dependent pressure acoustics analyses Review and further use two new tutorial models coupling vibrations with noise in a gearbox and an induction motor
COMSOL 5.3 TUTORIAL SIMULATOR
Review and manipulate a new Rotor Bearing System Simulator app for rotordynamics Utilize the new Lemaitre-Chaboche viscoplastic material model Enact stress linearization evaluations for pressure vessels Quickly assess the need for elastoplastic analyses on components through calculating safety factors in linear elastic analyses Develop models involving self-equilibrating loads more easily with automatic constraints of rigid body motions New Acoustics Module Features in COMSOL 5.3 Webinar May 23 Use the new Schrödinger Equation interface for quantum mechanical computations in 1D, 2D, and 3D Import photometric data files for ray optics modeling Apply automatic termination of rays in ray optics models by employing user-defined bounding boxes or intensity drops Utilize a new Part Library for standard RF and microwave components Review and manipulate a new permanent magnet motor tutorial model Perform fast capacitance and general lumped matrix calculations with a new study type Model electrostatics applications with a new physics interface based on the boundary element method, which can also be combined with finite element method modeling
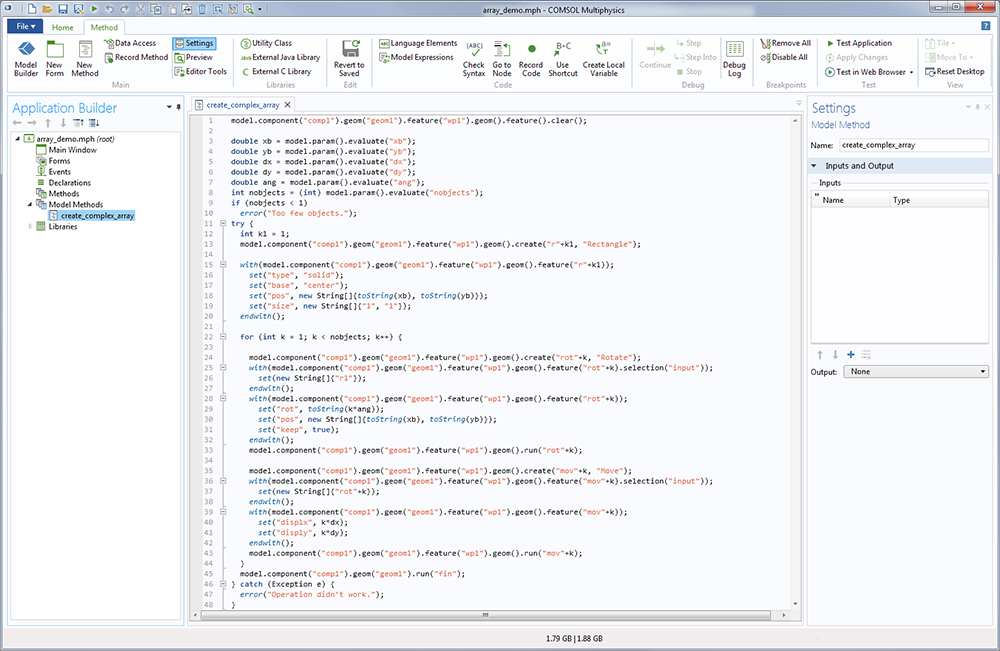
Generate adaptive meshes that are integrated with user-defined mesh sequences Combine two time-dependent or parametric solutions into one for further use Receive suggestions for direct and iterative solvers for choosing between fast or memory-conservative solutions Visualize specific and important parts of 3D plots through filters based on selections Simultaneously visualize different parameter values of different scales on the dual y-axes of 1D plots Automatically remove small geometric details to provide more robust meshes

Automatic generation of pyramid element transition layers between hex, prism, and tet meshes Better administrate centralized cluster settings and user log files in the COMSOL Server™ product Perform customized actions when clicking on plots in Graphics form objects in apps Use the newly available Model method functionality in the Model Builder to automate and manipulate a large number of modeling tasks These are most noticeable when working with models made up of a variety of several thousand domains, boundaries, edges, and points. Version 5.3 makes it more efficient to create models and deploy and run apps.ĬOMSOL Multiphysics version 5.3 provides significant performance improvements as compared to version 5.2a and earlier versions.
COMSOL 5.3 TUTORIAL SOFTWARE
You will experience speedup by a factor of up to ten in software responsiveness, as well as new and improved features for solving, meshing, and the physics-based add-on modules. This release provides you with notable performance improvements as compared to earlier versions.

COMSOL, the leading provider of multiphysics modeling and simulation software, has released version 5.3 of COMSOL Multiphysics software, is a general-purpose software platform, based on advanced numerical methods, for modeling and simulating physics-based problems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
